Introduction
When people talk about "investments," they usually mean buying stock in a company or providing funding for a business venture. Personal business investments are distinct from these but serve a similar purpose: to boost profits. Investing looks very different depending on the sector you operate in. Investments don't always need to be physical things like brand-new machinery or higher-quality raw materials.
The rate of return on an investment (ROI) is a common metric for gauging an asset's profitability and usefulness as an investment. To put it simply, return on investment (ROI) is an attempt to quantify the financial gain made from expenditure about that expenditure's price tag. The investment return on investment (ROI) is determined by dividing the total gain from an investment by its initial outlay. A percentage or ratio is used to represent the result.
Returns On Investment Formula
Several different ROI calculations are possible. The two most frequent applications are demonstrated below:
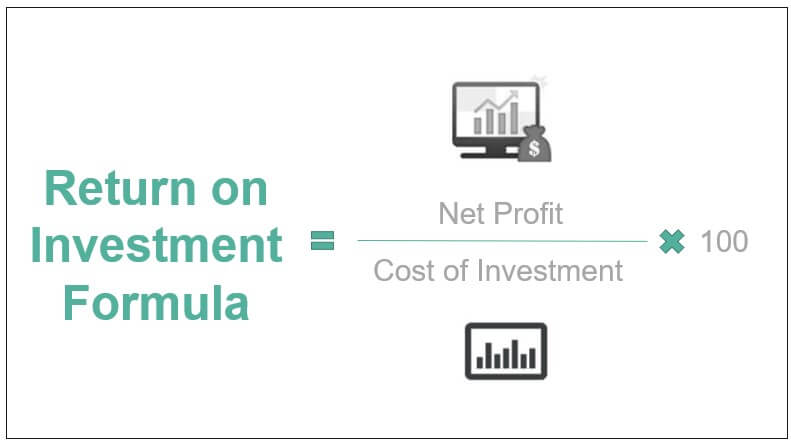
- Return on Investment (ROI) = Profit After Taxes / Expenses (or Gain on Investment / Initial Investment).
The original formula is the most widely employed ROI ratio (net income/cost of an investment). The Return on Investment (ROI) formula can be thought of as simply taking the "benefit" and dividing it by the "cost." Probing for specifics when someone claims something has a good or bad return on investment (ROI) is important.
Use of the ROI Formula Calculation
Simple calculations of return on investment can aid a potential investor in deciding whether or not to pursue a given investment opportunity. The calculation result may also serve as a measure of the investment's success thus far. A positive or negative return on investment (ROI) can be an instructive indicator of the value of an investment. Investors use return on investment (ROI) calculations to identify profitable investments. Investors and portfolio managers can use this strategy to strive for optimal returns.
Benefits of the ROI Formula
The many uses of the return on investment ratio should be well-known to any analyst.
Simple and Easy to Calculate
The ROI metric is popular because of how simple it is to compute. We need only two numbers: the gain and the expenditure. The Return on Investment (ROI) formula is simple to implement because there is no universally accepted definition of "return."
Universally Understood
If you use the term "return on investment" in casual conversation, it's safe to assume that your listeners will have a basic understanding of the concept.
Limitations of the ROI Formula
While the ratio is often helpful, it's important to know the caveats associated with the ROI calculation. Two major considerations are outlined below.
The ROI Formula Disregards the Factor of Time
An investment's return on investment (ROI) may not indicate how well it performs. Suppose that the rate of return on two different investments is equal, at 50%. While the first investment pays off in three years, the second takes five years to reach the same point. Since both investments yielded the same return on investment, it was difficult to tell which was the better choice; however, once the time was taken into account, the winner became clear. To make a fair comparison, the investor must examine both instruments using the same time frame and market conditions.
The ROI Formula is Susceptible to Manipulation
Both you and your coworker will get different results from an ROI calculation if you use different formulas. A marketer can use the property calculation detailed in the example section without factoring in expenses like upkeep, taxes, sales commissions, stamp duties, or legal fees. The real return on investment (ROI), taking into account all costs, is what an investor should focus on.

Conclusion
Simply put, return on investment (ROI) is a simple and straightforward way to evaluate the success of a financial venture. This common analysis method ensures that all investment choices are compared equally. Return on investment (ROI) is useful. Still, it is not sufficient for decision-making because it requires an accurate accounting of all costs and does not consider the investment's risk or time horizon. Return on investment (ROI) can be useful, but it shouldn't be your only metric of choice when assessing a purchase.
Calculating return on investment is more of an approximation than a precise measurement tool. To maximise return on investment, more precise projections are always welcome. Learning how to calculate the return on investment for a business endeavour is an important skill. Many businesses rely on return on investment (ROI) analysis to determine which promotional strategies are most profitable. Thus, return on investment (ROI) can be used as a forecast for the next few months and a measure of past success.









